Understanding Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary Tract Infections, or UTIs, are a common issue that affects millions of people worldwide. These infections occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract and begin to multiply, causing a variety of symptoms such as pain, frequent urination, and discomfort. In this section, we'll delve into the basics of UTIs, their symptoms, causes, and how they are typically treated. By understanding the fundamentals of UTIs, we can better explore the potential connection between these infections and bladder cancer.
Recognizing the Symptoms of UTIs
Urinary Tract Infections can manifest in different ways, but some of the most common symptoms include a strong, persistent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, and cloudy, dark, or strong-smelling urine. Other possible symptoms may include lower abdominal pain, feeling tired or shaky, and even a low-grade fever. Recognizing these symptoms early on is crucial for timely treatment and recovery, as well as reducing the risk of complications such as kidney infections or, as we will discuss later, bladder cancer.
Causes and Risk Factors of UTIs
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of a UTI. The main cause is the presence of bacteria, most commonly Escherichia coli (E. coli), which can enter the urinary tract through the urethra. Other risk factors include a weakened immune system, urinary tract abnormalities, and use of urinary catheters. Additionally, women are more likely to develop UTIs due to their shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventative measures to reduce their chances of developing a UTI.
Diagnosis and Treatment of UTIs
Diagnosing a UTI typically involves a urine test to detect the presence of bacteria and white blood cells, which are signs of an infection. Once a UTI has been diagnosed, treatment usually consists of a course of antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. It's important to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished, to ensure the infection is fully treated and to prevent recurrence. Drinking plenty of water and using over-the-counter pain relievers can also help alleviate symptoms during treatment.
Preventing UTIs
There are several steps individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing a UTI. These preventative measures include drinking plenty of water, wiping from front to back after using the toilet, urinating soon after intercourse, and avoiding potentially irritating feminine products. By practicing good hygiene and taking these precautions, the risk of developing a UTI can be significantly reduced.
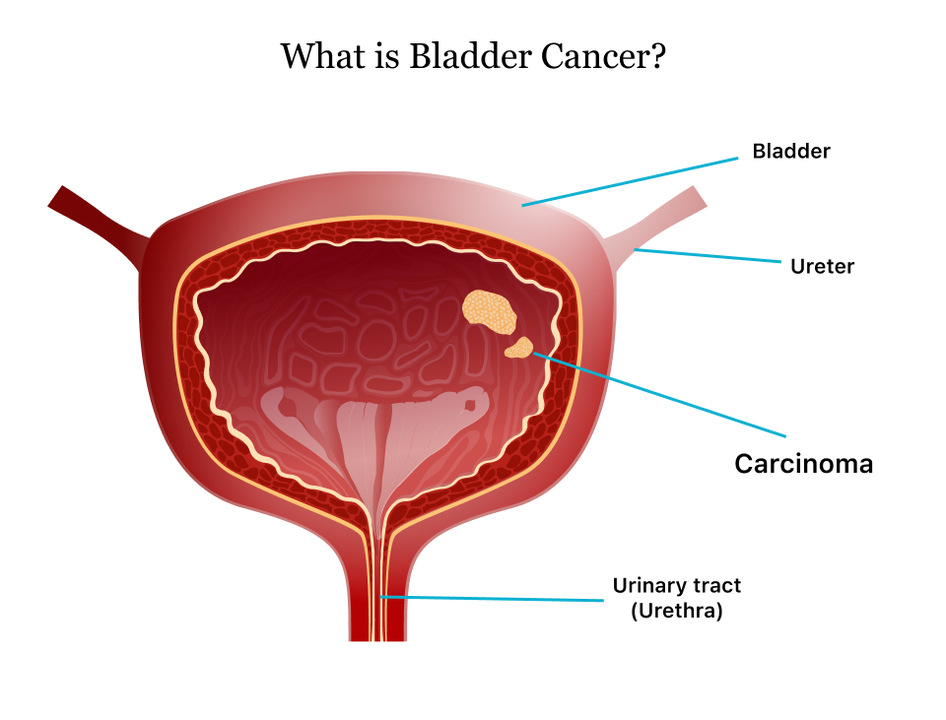
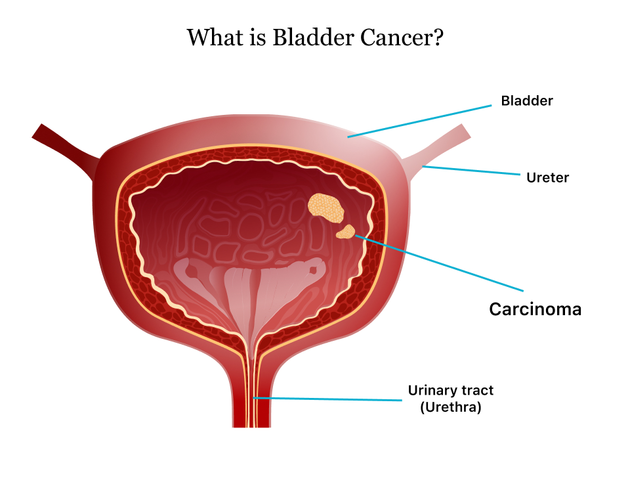
Understanding Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the cells lining the inside of the bladder. It is the sixth most common cancer in the United States, and risk factors include smoking, exposure to certain chemicals, and a family history of the disease. Symptoms of bladder cancer can be similar to those of a UTI, such as blood in the urine, pain during urination, and frequent urination. In this section, we will explore the potential connection between UTIs and bladder cancer, and how these two conditions may be related.
Chronic Inflammation and Cancer
One possible explanation for the connection between UTIs and bladder cancer is the role of chronic inflammation. When the body experiences a UTI, the immune system responds with inflammation to fight off the infection. However, if UTIs occur frequently or are not properly treated, this inflammation can become chronic, leading to damage and changes in the cells lining the bladder. Over time, these changes can increase the risk of developing bladder cancer. This highlights the importance of properly diagnosing and treating UTIs to prevent complications such as chronic inflammation and the potential development of bladder cancer.
UTIs and Bladder Cancer: A Direct Link?
While there is evidence to suggest a connection between chronic inflammation and cancer, it is important to note that having a UTI does not directly cause bladder cancer. UTIs are a common condition, and the vast majority of individuals who experience them will not go on to develop bladder cancer. However, the presence of chronic inflammation and other factors, such as those mentioned previously, can increase an individual's risk of developing the disease. As a result, it is important to be aware of the potential connection between UTIs and bladder cancer and take appropriate measures to prevent and treat infections.
Reducing the Risk of Bladder Cancer
While the connection between UTIs and bladder cancer may not be direct, there are still steps individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing the disease. These measures include quitting smoking, limiting exposure to harmful chemicals, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle through regular exercise and a balanced diet. Additionally, taking steps to prevent UTIs and seeking prompt treatment if they do occur can help reduce the risk of chronic inflammation and its potential complications, including bladder cancer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while there is no direct link between UTIs and bladder cancer, there is a potential connection through the presence of chronic inflammation. By understanding the causes and symptoms of UTIs, as well as the risk factors for bladder cancer, individuals can take appropriate measures to prevent and treat infections and reduce their risk of developing bladder cancer. As always, it is important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any concerning symptoms or have questions about your health.

L Walker
May 27, 2023 AT 21:53giri pranata
May 28, 2023 AT 08:31Stuart Rolland
May 28, 2023 AT 21:02Kent Anhari
May 29, 2023 AT 11:54Charlos Thompson
May 30, 2023 AT 09:56Peter Feldges
May 30, 2023 AT 11:59Richard Kang
May 30, 2023 AT 22:59Rohit Nair
May 31, 2023 AT 08:49Wendy Stanford
May 31, 2023 AT 15:40Jessica Glass
June 1, 2023 AT 02:28Krishna Kranthi
June 1, 2023 AT 21:33Lilly Dillon
June 1, 2023 AT 23:18Shiv Sivaguru
June 2, 2023 AT 06:22Gavin McMurdo
June 2, 2023 AT 15:47Jesse Weinberger
June 3, 2023 AT 03:48Emilie Bronsard
June 3, 2023 AT 15:34John Bob
June 4, 2023 AT 09:48George Johnson
June 5, 2023 AT 08:28