Kidney Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and How Medications Affect Your Kidneys
When your kidney disease, a condition where the kidneys lose their ability to filter waste and excess fluid from the blood. Also known as chronic kidney disease, it often creeps up slowly, with few early signs—until things get serious. Your kidneys don’t just make urine. They regulate blood pressure, balance electrolytes, produce red blood cell stimulants, and remove drugs and toxins. When they start failing, everything else in your body feels it.
Many people with kidney disease don’t know it until they’re in stage 3 or 4. Common red flags? Swelling in the ankles, constant fatigue, trouble sleeping, poor appetite, or foamy urine. But here’s what most don’t realize: diuretics, medications that help your body get rid of extra fluid like furosemide or hydrochlorothiazide are often used to manage symptoms—but they can also strain kidneys if not dosed right. And fluid retention, the buildup of excess fluid in tissues isn’t just uncomfortable—it’s a direct sign your kidneys are struggling to keep up.
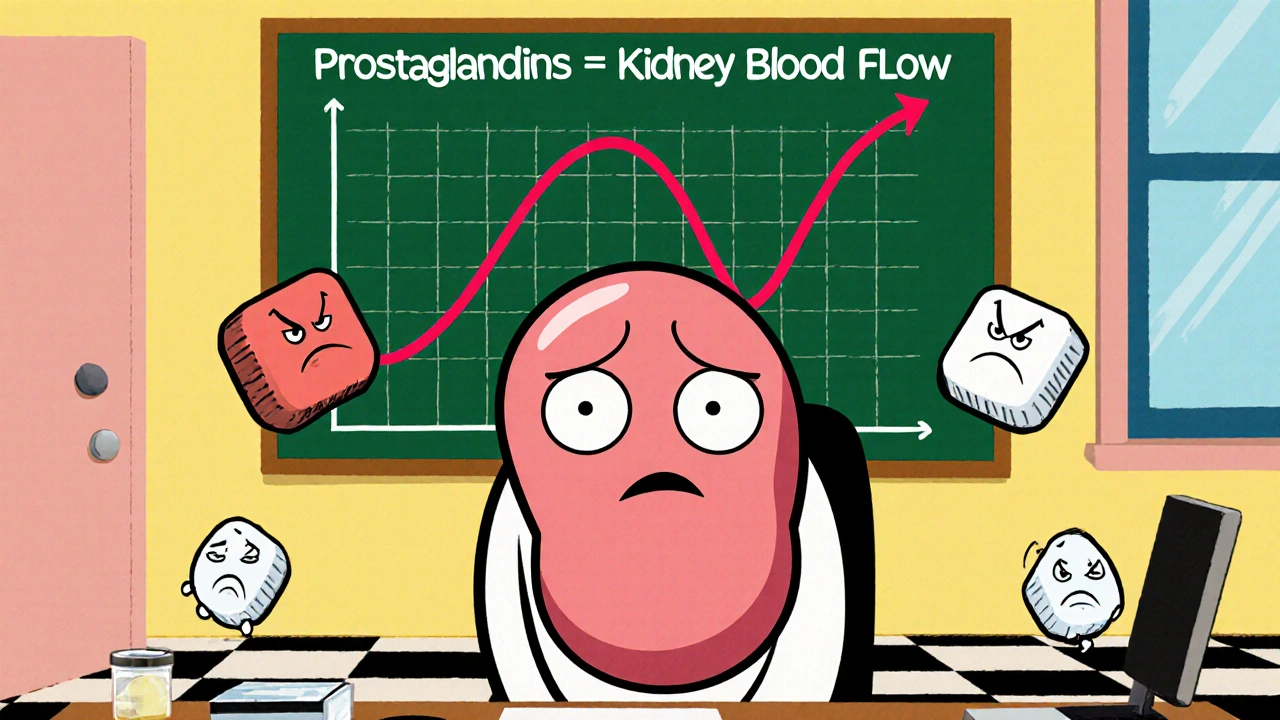
Some meds that help one thing can hurt your kidneys. DPP-4 inhibitors for diabetes? Linked to joint pain, but also kidney stress in some users. Blood pressure drugs like losartan or valsartan? They protect kidneys in the long run—but only if you’re monitored. Even common painkillers like ibuprofen can reduce kidney blood flow if taken daily. And don’t forget biotin supplements—high doses can mess with lab tests that check kidney function, leading to wrong diagnoses.
What you’ll find here isn’t just theory. These posts are from real people dealing with kidney issues, their meds, and what actually works. You’ll see how hydration affects swelling, why some diuretics work better than others, and how other conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes tie into kidney health. No fluff. No guesses. Just what you need to ask your doctor, understand your labs, and protect your kidneys before it’s too late.
 20 Nov 2025
20 Nov 2025
NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen can cause acute kidney injury, especially in people with existing kidney disease or other risk factors. Learn how to use them safely and what alternatives work better.
View More

