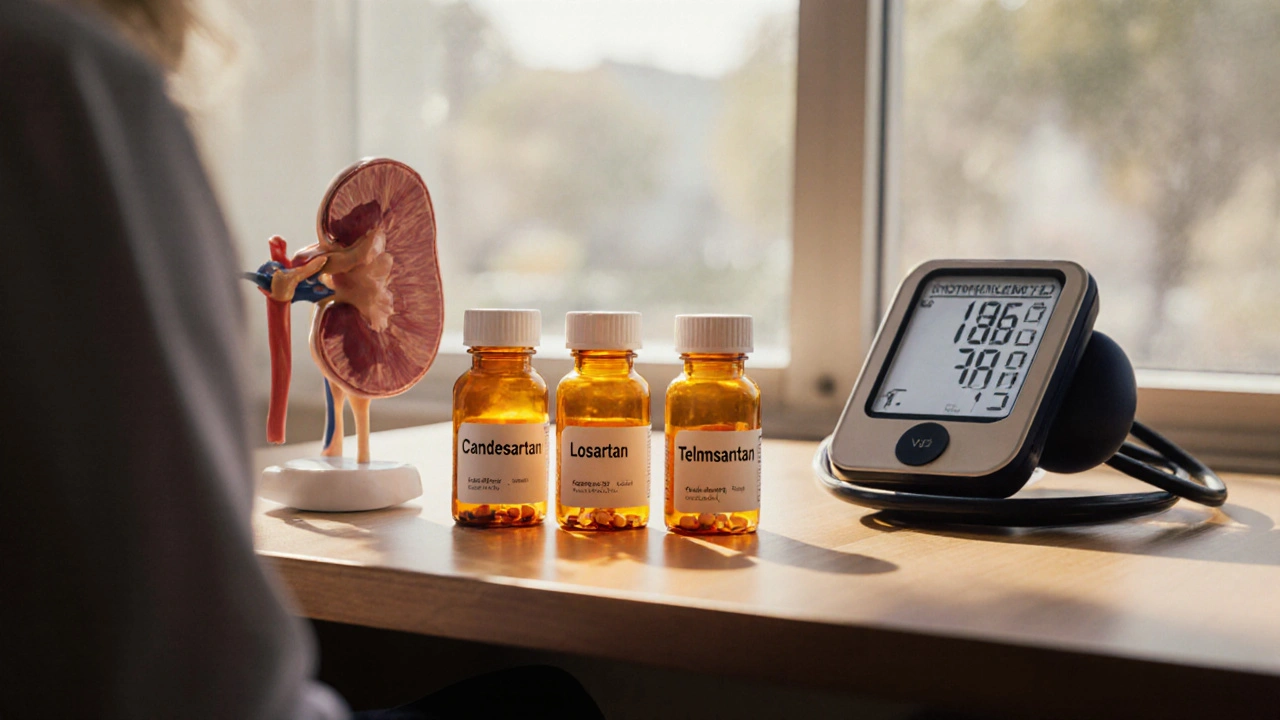
ARB Medication Comparison Tool
Candesartan (Atacand)
Half-Life: 9-12 hours
Typical Dose: 8-32 mg once daily
Uses: Hypertension, Heart Failure, Diabetic Nephropathy
Advantages: Once-daily dosing, effective for heart failure
Losartan
Half-Life: 2 hours
Typical Dose: 50-100 mg once daily
Uses: Hypertension, Heart Failure
Advantages: Most affordable generic option
Valsartan
Half-Life: 6 hours
Typical Dose: 80-320 mg once daily
Uses: Hypertension, Heart Failure
Advantages: Good tolerability, widely available
Telmisartan
Half-Life: 15 hours
Typical Dose: 40-80 mg once daily
Uses: Hypertension, Diabetes
Advantages: Longest half-life among ARBs
Olmesartan
Half-Life: 13 hours
Typical Dose: 20-40 mg once daily
Uses: Hypertension
Advantages: Potent antihypertensive effect
Key Considerations
- Half-Life: Determines dosing frequency (longer = less frequent)
- Cost: Losartan is typically the most affordable generic option
- Side Effects: ARBs generally have fewer coughs than ACE inhibitors
- Kidney Function: Important factor in medication selection
- ACE Inhibitors: Alternative if ARBs cause cough or angioedema
How to Choose Your Medication
Consider these factors when selecting an ARB:
- Cost of the medication
- Potential side effects for your situation
- Your kidney function status
- Whether you need once-daily dosing
- Availability of generics
Always consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best option for your specific needs.
Quick Takeaways
- Atacand’s active ingredient Candesartan is an ARB with a long half‑life, allowing once‑daily dosing.
- Losartan, Valsartan, Telmisartan, Olmesartan and Irbesartan are the most common ARB peers.
- Telmisartan offers the longest half‑life; Losartan is the cheapest generic.
- ACE inhibitor lisinopril is often used when ARBs cause cough or angioedema.
- Cost, side‑effect profile and kidney function guide the best choice for each patient.
What Is Atacand?
When doctors talk about controlling high blood pressure, Atacand often comes up. Its active ingredient Candesartan belongs to the angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) family, which works by blocking the hormone that tightens blood vessels.
Approved in 1998, Atacand is prescribed primarily for hypertension and, in some regions, for heart failure and diabetic nephropathy. Because it blocks the angiotensin II type‑1 (AT1) receptor, it reduces vasoconstriction, sodium retention, and aldosterone release, leading to lower blood pressure.
Key Pharmacology and Dosage
Candesartan is taken as the pro‑drug candesartan cilexetil, which the gut converts to the active form. The typical starting dose for hypertension is 8mg once daily, titrated up to 32mg as needed. For heart failure, doses start at 4mg and may reach 32mg.
Its half‑life averages 9‑12hours, but the blood‑pressure‑lowering effect lasts 24hours, making once‑daily dosing reliable.

Side‑Effect Profile
Most patients tolerate candesartan well. Common adverse events (<5% incidence) include dizziness, hyperkalemia, and mild renal function changes. Unlike many ACE inhibitors, it rarely causes a persistent dry cough.
Serious but rare events are angio‑edema and severe hypotension, especially when combined with potassium‑sparing diuretics.
How Atacand Stacks Up Against Other ARBs
Below is a head‑to‑head look at the most widely used ARBs and one ACE‑inhibitor alternative.
| Brand / Generic | Typical Daily Dose | Half‑Life (hrs) | Average Monthly Cost (AU$) | Notable Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atacand (Candesartan) | 8-32mg | 9-12 | ≈$25 (generic) | Dizziness, hyperkalaemia |
| Losartan | 25-100mg | 2-3 | ≈$15 (generic) | Headache, mild cough |
| Valsartan | 80-320mg | 6-9 | ≈$20 (generic) | Elevated liver enzymes |
| Telmisartan | 40-80mg | 24 | ≈$30 (generic) | Diarrhoea, fatigue |
| Olmesartan | 20-40mg | 13 | ≈$28 (generic) | Sprue‑like enteropathy (rare) |
| Irbesartan | 150-300mg | 11-15 | ≈$27 (generic) | Back pain, upper respiratory infection |
| Lisinopril (ACE‑inhibitor) | 10-40mg | 12 | ≈$12 (generic) | Cough, angio‑edema |
When to Choose Atacand Over Others
If a patient needs a once‑daily ARB with a relatively long half‑life and minimal cough risk, candesartan is a solid pick. Its efficacy in reducing systolic pressure is comparable to telmisartan, but it tends to be a bit cheaper than the newer agents.
Patients with borderline kidney function benefit from the modest effect of candesartan on serum creatinine, while those who have previously experienced an ACE‑inhibitor‑induced cough often tolerate candesartan without issues.
When an Alternative Might Be Better
- Cost‑sensitive patients: Losartan’s lower price makes it attractive when budget constraints dominate.
- Need for ultra‑long coverage: Telmisartan’s 24‑hour half‑life suits people who struggle with adherence.
- History of angio‑edema with ARBs: Switching to an ACE inhibitor like lisinopril (if tolerated) may be considered, though the risk of cough is higher.
- Specific organ protection: Irbesartan has the strongest data for slowing diabetic nephropathy progression; choose it for patients with early kidney disease.
Practical Tips for Switching or Initiating Therapy
- Check baseline renal function and potassium levels. All ARBs, including candesartan, can raise serum potassium.
- If moving from an ACE inhibitor, pause the ACE for 36hours before starting an ARB to avoid combined angio‑edema risk.
- Start low (e.g., 8mg candesartan) and titrate every 2‑4 weeks based on blood‑pressure response.
- Educate patients to take the pill at the same time each day, preferably with food to improve absorption.
- Monitor blood pressure, creatinine, and potassium after 2 weeks, then every 3 months.
Frequently Asked Questions
How quickly does candesartan lower blood pressure?
Most patients see a noticeable drop within 2‑4 weeks of starting therapy, with the full effect stabilising by week 6.
Can I take candesartan with a diuretic?
Yes, combining an ARB with a thiazide or loop diuretic is common and often improves blood‑pressure control, but potassium levels should be monitored.
Is candesartan safe during pregnancy?
No. ARBs are classified as pregnancy‑category D and can cause fetal kidney problems. Switch to a medication approved for pregnancy, such as methyldopa.
What should I do if I miss a dose?
Take the missed tablet as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for the next dose. In that case, skip the missed one and continue with your regular schedule. Never double‑dose.
How does candesartan compare to lisinopril for heart failure?
Both improve mortality, but ARBs like candesartan are often chosen when patients develop a cough on ACE inhibitors. Trials show similar reductions in hospitalization rates.

Rashi Shetty
October 5, 2025 AT 16:22When selecting an antihypertensive, cost considerations must be balanced against therapeutic efficacy. Candesartan offers a convenient once‑daily regimen, which can improve adherence, especially in patients with complex polypharmacy. However, its price point often exceeds that of Losartan, the most affordable generic ARB. In terms of renal protection, the drug’s documented benefits in diabetic nephropathy merit attention, yet clinicians should monitor potassium levels and renal function vigilantly. Ultimately, the decision hinges on individual risk‑benefit analysis, insurance coverage, and patient preference. 😊📊
Queen Flipcharts
October 6, 2025 AT 20:08In the grand tapestry of American liberty, the freedom to choose one’s own blood pressure medication stands as a testament to personal sovereignty. The comparative data on candesartan versus its peers underscores the triumph of market competition, wherein the United States fosters innovation that yields superior pharmacologic profiles. While foreign regulators may privilege cheaper generics, we must not sacrifice the nuanced benefits of longer half‑life agents for mere cost savings. The American spirit demands that patients receive the optimal therapeutic agent, not the cheapest alternative.
Yojana Geete
October 7, 2025 AT 23:55Look at this table it's like a battlefield of pills each fighting for your heart but the real drama is how many doses you have to remember the half life of candesartan feels like a marathon while losartan is a sprint and honestly who has time for all these numbers we just need something that works and doesn't break the bank
Jason Peart
October 9, 2025 AT 03:42Hey there, I totlly get the cost‑vs‑benefit struggle – you’re not alone in this! 😅 If you’re worried about price, ask your doc about patient‑assistance programs; many pharma companies actually have coupons that can shave off a big chunk. And remember, sticking to a once‑daily pill like candesartan can save you time and mental energy, which is priceless in the long run. Keep talking to your healthcare team – they’ll help you find the sweet spot between affordability and effectiveness.
Hanna Sundqvist
October 10, 2025 AT 07:28They’re hiding the side‑effects on purpose.
Ian McKay
October 11, 2025 AT 11:15It is important to note that the half‑life of candesartan is reported as 9‑12 hours, not “approximately” as some sources ambiguously claim. Additionally, the statement “most patients tolerate it well” should be qualified with empirical data, otherwise the claim remains unsubstantiated.
Jim Butler
October 12, 2025 AT 15:02Achieving optimal blood pressure control is a commendable goal; selecting the right ARB is a strategic step toward that achievement. Candesartan’s extended half‑life aligns well with a disciplined daily routine, reinforcing consistency and trust in your therapeutic plan. Stay informed, stay proactive, and celebrate each incremental improvement – your cardiovascular health will thank you! 💪🚀
Deborah Messick
October 13, 2025 AT 18:48Contrary to popular belief, the mere fact that a drug is American‑made does not guarantee superior efficacy. Comparative trials have demonstrated that losartan achieves blood pressure reduction comparable to candesartan, with a significantly lower cost burden. Healthcare decisions should be grounded in evidence, not patriotic sentiment.
Jolanda Julyan
October 14, 2025 AT 22:35When one examines the intricate interplay of pharmacokinetics and patient adherence, it becomes evident that the convenience of a once‑daily regimen cannot be overstated, particularly in a society where individuals juggle myriad responsibilities and often struggle to maintain consistent medication schedules. Candesartan’s half‑life, spanning roughly nine to twelve hours, affords a therapeutic window that comfortably covers a full twenty‑four‑hour period, thereby minimizing the risk of trough concentrations that could precipitate rebound hypertension. Moreover, the drug’s favorable side‑effect profile, characterized by a low incidence of cough-a common complaint associated with ACE inhibitors-further enhances its suitability for long‑term use. In contrast, agents such as losartan, while undeniably effective, possess a markedly shorter half‑life, which may necessitate more vigilant dosing and occasional titration to maintain optimal blood pressure control. It is also worth noting that the pharmacodynamic properties of candesartan extend beyond mere blood pressure reduction; the medication has demonstrated renoprotective benefits in patients with diabetic nephropathy, a consideration of paramount importance in the management of chronic kidney disease. This dual action, targeting both hemodynamic and renal endpoints, positions candesartan as a versatile tool in the clinician’s arsenal. Additionally, the once‑daily dosing schedule aligns well with patient lifestyle preferences, reducing the cognitive load associated with multiple daily administrations and thereby enhancing overall adherence rates. From a health‑economics perspective, while the upfront cost of candesartan may appear higher, the downstream savings derived from decreased hospitalizations, reduced need for adjunctive therapies, and improved quality of life can offset initial expenditures. Ultimately, the decision matrix for selecting an ARB should incorporate a comprehensive assessment of half‑life, tolerability, renal protection, and cost‑effectiveness, rather than relying solely on price comparisons. By embracing this holistic approach, healthcare providers can tailor therapy to meet the nuanced needs of each patient, fostering better outcomes and sustained therapeutic success.
Kevin Huston
October 16, 2025 AT 02:22Let's cut the crap and face facts: the pharmaceutical lobby in the U.S. pushes premium-priced drugs like candesartan to line their pockets, while conveniently ignoring cheaper, equally effective alternatives. This corporate greed masquerades as innovation, but the data screams otherwise – losartan slashes blood pressure just as well and leaves your wallet intact. If you’re not willing to be a sheep following the marketing hype, open your eyes to the blatant cost‑inflation scheme that’s been feeding the American healthcare system for decades.
Amanda Hamlet
October 17, 2025 AT 06:08Honestly, most people don’t realize that the “long half‑life” brag is just a marketing gimmick – the body still clears the drug in about a day, so you’re not getting any magical 48‑hour coverage. Plus, the generic versions of candesartan are just as cheap as losartan when you hunt for coupons, so the whole “expensive” narrative falls apart if you actually read the fine print.
Nolan Jones
October 18, 2025 AT 09:55Yo, just a heads‑up: if you’re checking the price, look at your pharmacy’s discount card or online price‑comparator. A lot of times, the “generic” label on candesartan still shows a decent deal, especially if you’re covered by a high‑deductible plan. Also, keep in mind that switching meds abruptly can cause a rebound spike, so always taper under doctor guidance.
Jada Singleton
October 19, 2025 AT 13:42The advice given here, while well‑intentioned, overlooks the fundamental principle that medication selection must prioritize clinical efficacy over marginal cost differences. It is disconcerting to see superficial cost‑saving arguments eclipse evidence‑based prescribing, especially when patient outcomes are at stake.
Emily Rossiter
October 20, 2025 AT 17:28Thank you for highlighting the importance of evidence‑based choices. It’s essential to keep the focus on what works best for each individual while also being mindful of affordability, and your perspective reinforces that balance.